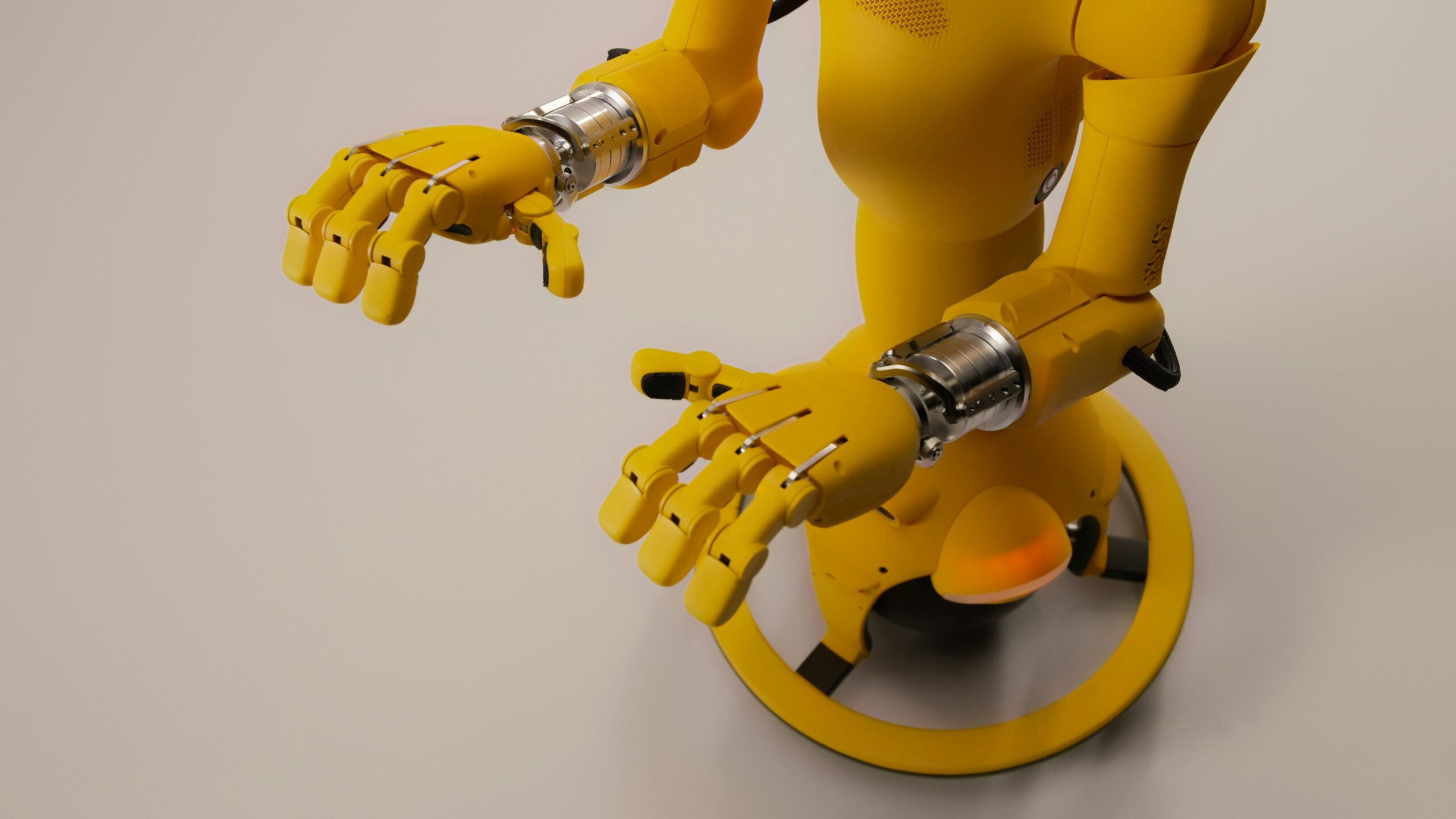
The evolution of artificial intelligence is accelerating beyond screens and virtual models into machines, robots, and other real-world systems — a transformation that was on full display at the Unikie Innovation Summit 2026 held in Tampere, Finland. The summit’s central theme was Physical AI Robotics, an emerging field that blends cognitive AI with physical embodiment, enabling machines not just to think but to act in the real world with autonomy and intelligence.
Physical AI isn’t a futuristic concept — it’s rapidly becoming a practical reality. At the summit, robotics, automation, and edge-based AI systems demonstrated how intelligence can be embedded directly into hardware and machines, turning them into autonomous, adaptive agents capable of solving real world tasks. These systems promise to transform industries from manufacturing and logistics to healthcare and infrastructure.
What Is Physical AI Robotics?
Physical AI Robotics refers to AI systems that go beyond software algorithms running in servers or phones; they interact with the physical world through sensors, control systems, and mechanical structures. In contrast to traditional cloud-based AI, these systems operate on edge devices — processing data locally for real-time perception, decision-making, and action.
At the Unikie Summit, this concept was defined as a broad umbrella that includes robotics, automation, and embedded intelligence capable of operating in unstructured environments — not just performing tasks but thinking and adapting as they go.
Key Highlights from the Summit
During the event, Unikie’s expo area showcased several hands-on Physical AI Robotics solutions that are already moving from research labs into practical use cases:
- Autonomous Machines: Robotics platforms equipped with onboard AI that can make decisions without relying on constant connectivity. These are especially useful in remote or network-limited environments where cloud dependency is impractical.
- Lights-Out Factory Models: Speakers at the summit described “lights-out” automation — manufacturing systems that run with minimal human oversight, using AI to handle operations, quality control, and safety monitoring.
- Edge AI for Real-Time Control: Representatives from industries like telecommunications, mining, and manufacturing emphasized the need for on-device AI and low-latency decision models that process data locally rather than sending it to central servers.
Why Physical AI Matters Today
The shift to Physical AI Robotics is more than a technological upgrade — it’s an industry transformation. Traditional AI based on cloud computation often suffers from latency, bandwidth limitations, and reliance on uninterrupted connectivity. In contrast, embodied AI systems process sensor data directly on hardware, enabling:
- Real-Time Decision Making: Robots and machines can adapt instantly to changing surroundings, essential for tasks like autonomous navigation and industrial inspection.
- Lower Latency and Higher Reliability: Edge-based AI systems reduce reliance on remote servers, making them more robust for safety-critical applications.
- Human-Machine Collaboration: Rather than replacing human workers, Physical AI Robotics augments capabilities, allowing experts to manage multiple sites remotely or focus on higher-level decision-making.
Industrial and Economic Impact
Physical AI Robotics could reshape entire sectors. For example:
- Manufacturing: AI-enabled robots that perform repetitive or dangerous tasks increase efficiency and reduce labor shortages while maintaining quality.
- Logistics: Autonomous mobile robots and AI-powered fleets can optimize supply chains, speeding deliveries and reducing human risk.
- Smart Infrastructure: Physical AI systems can monitor and adapt buildings, power systems, and transportation networks for safety and efficiency.

Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite rapid progress, hurdles remain. Embodied AI systems must meet strict safety standards and regulatory approvals before deployment, especially in healthcare or public domains. Robust cybersecurity frameworks are also necessary to protect physical AI from malicious interference.
Nevertheless, the momentum behind Physical AI Robotics suggests that these technologies will increasingly integrate into daily life and industrial operations. Events like the International Conference on Embodied Intelligence and Large Models 2026 highlight the academic and research focus on bridging the gap between AI theory and physical application.
Real-World AI, Real-World Impact
From robotics at major tech showcases like CES 2026 to specialized industry events such as the Unikie Summit, the era of Physical AI Robotics is no longer a distant future — it’s unfolding now. With real-world applications already in demonstration and deployment phases, the coming years could see significant transformations in how humans and machines collaborate across sectors.
This article is part of Ambuzzway Innovation coverage, reporting on breakthrough AI and robotics technologies around the world. Sources include official summit releases and global tech innovation analysis.